Polyethylene (PE) is a whitish, transparent to translucent thermoplastic material, and is often manufactured in thin, transparent sheets. Thick sections are translucent and have a waxy appearance. A wide variety of colored products can be obtained by using dyes.
Ethylene polymerization can produce products with a wide variety of physical properties. These products have the basic chemical structure ( – CH 2 – CH 2 – ) n in common , and generally have the chemical properties of a high molecular weight alkane. This type of polymer was created for use as electrical insulation, but has since found many applications in other fields, especially as a film and for packaging.
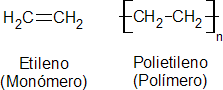
Types of Polyethylene
In general there are two types of polyethylene:
- Low density (LDPE)
- High density (HDPE).
Low-density polyethylene has a branched chain structure, while high-density polyethylene has essentially a straight chain structure.
Low-density polyethylene was first produced commercially in the United Kingdom in 1939 using autoclave (or tubular) reactors requiring pressures of 14,500 psi (100 MPa) and temperatures of about 300 ºC. High-density polyethylene was first produced commercially in 1956-1959 by the Philips and Ziegler processes using a special catalyst. In these processes the pressure and temperature for the reaction converting ethylene to polyethylene were considerably lower. For example, the Philips process operates at 100 to 150 ºC and 290 to 580 psi (2 to 4 MPa) pressure.

A new, simplified low-pressure process for the production of polyethylene was developed around 1976, using a pressure of 100 to 300 psi (0.7 to 2 MPa) and a temperature of about 100 ºC. The polyethylene produced can be described as linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) and has a straight chain structure with short, inclined side branches.
General Considerations
Thermoplastics can be repeatedly softened by heating and hardened by cooling. Polyethylene resins are thermoplastic.
The properties of polyethylene resins are due primarily, if not exclusively, to three basic molecular properties: density, average molecular weight, and molecular weight distribution. These basic properties in turn depend on the size, structure, and uniformity of the polyethylene molecule. Some of the properties that make polyethylene such a desirable raw material for thousands of manufactured items include light weight, flexibility, toughness, high chemical resistance, and outstanding electrical properties.

The intense competition in the polyethylene market has brought with it increased work on modifying polyethylenes with specific properties for particular applications. Improvements in properties for particular uses are expected as the structure of the various polyethylene polymers and their relationship to physical and chemical properties become better understood.